By: CS2103-AY1819S2-W15-2 Since: Feb 2019
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. GUI Components
- 4. Features
- 5. Commands
- 5.1. Viewing help :
help - 5.2. Listing expenses :
listexpense - 5.3. Adding an expense:
addexpense - 5.4. Editing an expense :
editexpense - 5.5. Deleting an expense :
deleteexpense - 5.6. Selecting an expense :
selectexpense - 5.7. Clearing all expense entries :
clearexpense - 5.8. Adding a budget :
addbudget - 5.9. Editing a budget:
editbudget - 5.10. Deleting a budget:
deletebudget - 5.11. Selecting a budget:
selectbudget - 5.12. Clearing all budgets:
clearbudget - 5.13. Listing debts:
listdebt - 5.14. Adding a debt:
adddebt - 5.15. Editing a debt:
editdebt - 5.16. Deleting a debt:
deletedebt - 5.17. Selecting a debt:
selectdebt - 5.18. Clearing all debts:
cleardebt - 5.19. Paying off a debt:
paydebt - 5.20. Listing recurrings :
listrecurring - 5.21. Adding a recurring:
addrecurring - 5.22. Editing a recurring :
editrecurring - 5.23. Deleting a recurring:
deleterecurring - 5.24. Selecting a recurring :
selectrecurring - 5.25. Clearing all recurrings:
clearrecurring - 5.26. Converting outstanding expenses from all recurrings:
convertrecurring - 5.27. Viewing Statistics - Summary:
stats - 5.28. Viewing Statistics - Trend:
statstrend - 5.29. Viewing Statistics - Compare:
statscompare - 5.30. Listing entered commands :
history - 5.31. Undoing previous command :
undo - 5.32. Redoing the previously undone command :
redo - 5.33. Exiting the program :
exit - 5.34. Saving the data
- 5.1. Viewing help :
- 6. Coming in v2.0
- 7. FAQ
- 8. Command Summary
1. Introduction
Personal Finance Tracker is for those who prefer to use a desktop app for expense tracking. More importantly, Personal Finance Tracker is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). Whether if you are an expert user or a non tech savvy user, we have commands that cater towards you guys!Interested? Jump to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started. Enjoy!
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
main.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Personal Finance Tracker.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
listexpensev/all: lists all contacts -
addexpensen/Sofa $/200 c/UTILITIES: adds an expense namedSofaof amount$200and category ofUTILITIESto the Finance Tracker. -
deleteexpense3: deletes the 3rd expense shown in the current list -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 5, “Commands” for details of each command.
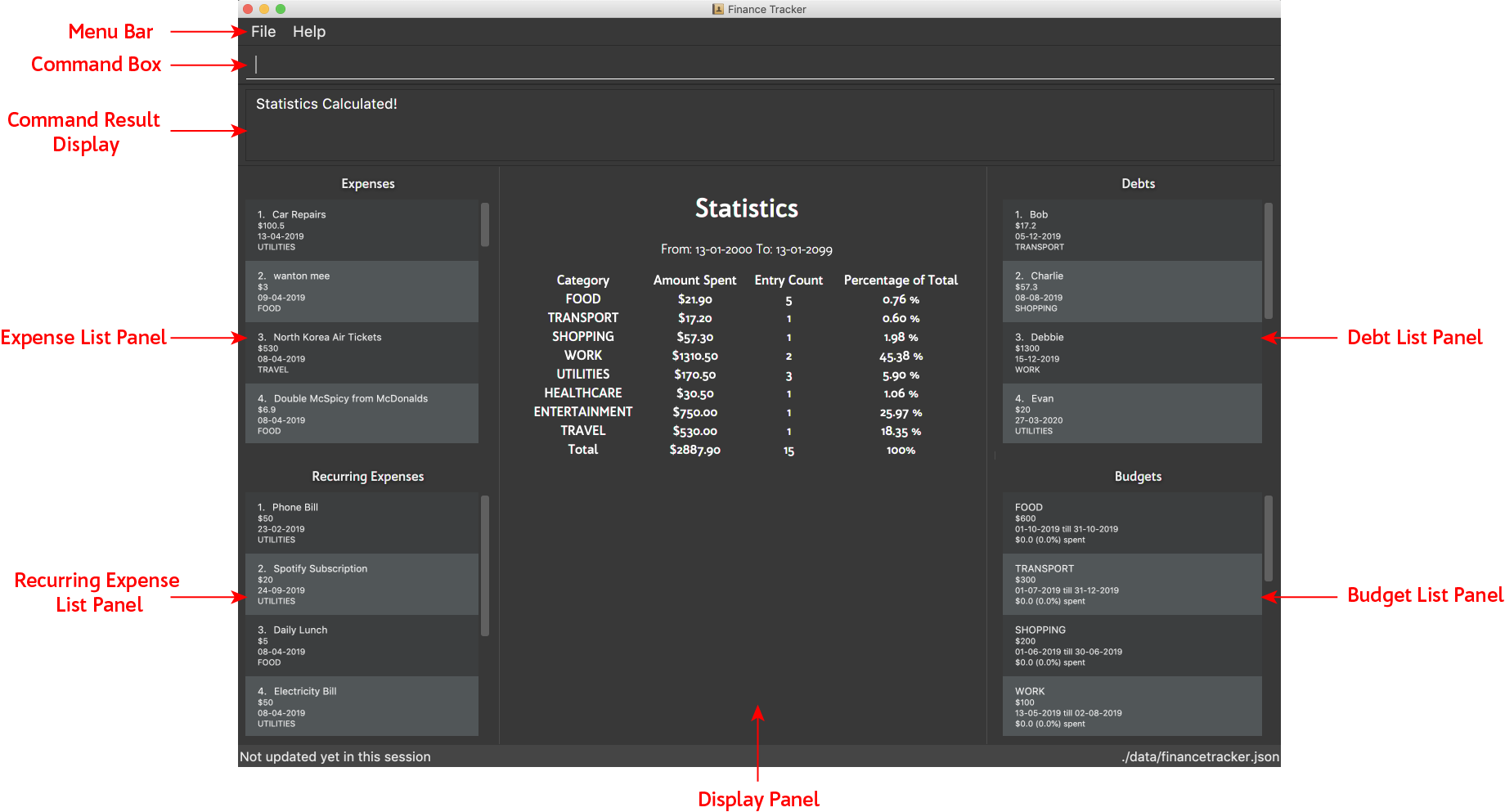
3. GUI Components
Personal Finance Tracker GUI consists of 5 main components that you can interact with:
-
Menu Bar: contains exit and help window function.
-
Command Box: textbox that receives your input commands.
-
Command Result Display: panel that displays the result of inputted commands.
-
Multiple List Panels: list panels that displays the list of expenses, recurring expenses, debts and budgets that are added by you.
-
Display Panel: panel displaying additional information for a selected entry as well as statistical information on expenses.
4. Features
4.1. Expense
Want to start tracking your expenses but don’t know what application to use?
Fret not, our Finance Tracker allows you to track your expenses by adding it into our system.
You can even categorise your expenses in terms of food, travel, transport and more!
4.2. Budget
Trying to save up for that upcoming trip?
The Budget feature helps you stay within your desired level of expenses within a specified time period!
You can even set budgets for specific categories to better manage your expenses!
4.3. Debt
Always losing track of payments due, personal loans or debts owed?
With the Debt feature, you’ll never forget your payments due ever again!
The Debt feature helps you to make expenses in advance and helps you keep track of these expenses due.
4.4. Recurring
Want to keep track of monthly bills in the expense tracker as well?
The Recurring feature simplifies the process of adding periodic expenses such as phone bills or Netflix subscriptions.
Instead of manually adding the same expense repetitively, just add a Recurring and the Finance Tracker will automatically
add the expense for you periodically at your specified frequency and for your specified duration!
4.5. Stats
Want to see trends and statistics of your expenses?
The Stats feature allows you to view a variety of statistics based on the expenses you’ve input into the Finance Tracker.
These statistics will help you better understand your expenses and make effective changes to your habits if so desired.
5. Commands
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inaddexpense n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asaddexpense n/Hamburger. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [r/REMARK]can be used in either of these forms:-
n/Hamburger r/lunch -
n/Hamburger
-
-
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY,$/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Repeated parameters e.g. n/NAME n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY are not acceptable.
5.1. Viewing help : help
Format: help
5.2. Listing expenses : listexpense
Shows a list of expenses in the finance tracker according to the view specified.
Format: listexpense v/VIEW
Shortcut: le v/VIEW
-
The VIEW specifies how the list of expenses are displayed.
-
v/all: displays entire list of expenses.
-
v/day: displays list of expenses with date within a day ago.
-
v/month: displays list of expenses with date within a month ago.
-
v/year: displays list of expenses with date within a year ago.
-
v/CATEGORY: displays list of expenses with CATEGORY such as FOOD, TRANSPORT, SHOPPING, WORK, UTILITIES, HEALTHCARE, ENTERTAINMENT, TRAVEL, OTHERS which are case insensitive.
-
v/$10, v/$100, v/$1000: display list of expenses with amount greater than or equal to $10, $100 or $1000.
-
5.3. Adding an expense: addexpense
Adds an expense to the finance tracker.
Format: addexpense n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
Shortcut: ae n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
-
The NAME should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
-
The AMOUNT should only contain positive numbers and reflect the value in dollars. Values accepted are in the range of $0.01 to $9,999,999.99. A maximum of 2 decimal places are allowed.
-
The CATEGORY is case insensitive and should only be one of the following: FOOD, TRANSPORT, SHOPPING, WORK, UTILITIES, HEALTHCARE, ENTERTAINMENT, TRAVEL, OTHERS.
-
The DATE should be in dd-mm-yyyy format.
-
If DATE is omitted, current date will be used.
-
If REMARK is omitted, no remarks will be stored.
| You can omit [optional] parameters by leaving them empty. |
Examples:
-
addexpense n/BKT $/3.00 c/food d/13-01-2019 r/My weekly bak kut teh intake. -
ae n/Sofa $/200 c/UTILITIES
5.4. Editing an expense : editexpense
Edits an existing expense in the finance tracker.
Format: editexpense INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
Shortcut: ee INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
-
Edits the expense at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed expense list. The index must be a positive integer.
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
| You can omit [optional] parameters by leaving them empty. If all parameters are empty, no edits will occur. |
Examples:
-
editexpense 9 $/450 c/food
Edits the amount and category of the 9th expense to be450andfoodrespectively.
5.5. Deleting an expense : deleteexpense
Deletes the specified expense from the finance tracker.
Format: deleteexpense INDEX
Shortcut: de INDEX
-
Deletes the expense at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed expense list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
-
listexpense v/all
deleteexpense 2
Deletes the 2nd expense in the finance tracker.
5.6. Selecting an expense : selectexpense
Select the specified expense from the finance tracker.
Format: selectexpense INDEX
Shortcut: se INDEX
-
Selects the expense at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed expense list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
-
listexpense v/all
selectexpense 2
Selects the 2nd expense in the finance tracker.
5.7. Clearing all expense entries : clearexpense
Clears all expense entries from the finance tracker.
Format: clearexpense
Shortcut: ce
5.8. Adding a budget : addbudget
Adds a budget with a time frame to the tracker.
Format: addbudget $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [sd/START_DATE] ed/END_DATE [r/REMARKS]
Shortcut: ab $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [sd/START_DATE] ed/END_DATE [r/REMARKS]
-
The categories include: FOOD, TRANSPORT, SHOPPING, WORK, UTILITIES, HEALTHCARE, ENTERTAINMENT, TRAVEL, OTHERS which are case insensitive.
-
The program only limits one budget for each category.
-
START_DATE and END_DATE must be in dd-mm-yyyy format.
-
If START_DATE is omitted, current date will be used.
Examples:
-
addbudget c/food $/400 sd/01-02-2019 ed/28-02-2019 -
ab c/others $/12000 sd/01-01-2019 ed/31-12-2019
5.9. Editing a budget: editbudget
Edits a budget in the finance tracker.
Format: editbudget c/CATEGORY [$/AMOUNT] [sd/NEW_START_DATE] [ed/NEW_END_DATE]
Shortcut: eb c/CATEGORY [$/AMOUNT] [sd/NEW_START_DATE] [ed/NEW_END_DATE]
|
Examples:
-
editbudget c/food ed/31-03-2019 -
eb c/others $/5000 sd/01-01-2019 ed/31-03-2019
5.10. Deleting a budget: deletebudget
Deletes a budget from the finance tracker.
-
Deletes the budget of the specified
CATEGORY.
Format: deletebudget c/CATEGORY
Shortcut: db c/CATEGORY
Examples:
-
deletebudget c/food
5.11. Selecting a budget: selectbudget
Selects a budget in the finance tracker.
-
Selects the budget of the specified
CATEGORY.
Format: selectbudget c/CATEGORY
Shortcut: sb c/CATEGORY
Examples:
-
selectbudget c/work
5.12. Clearing all budgets: clearbudget
Clears all budgets from the finance tracker.
Format: clearbudget
Shortcut: cb
5.13. Listing debts: listdebt
Shows a list of debts in the finance tracker according to the view specified.
Format: listdebt v/VIEW
Shortcut: ld v/VIEW
-
The VIEW specifies how the list of debts is displayed.
-
v/all: displays entire list of debts
-
v/day: displays list of debts with deadline in a day
-
v/week: displays list of debts with deadline in a week
-
v/month: displays list of debts with deadline in a month
-
v/year: displays list of debts with deadline in a year
-
v/CATEGORY: displays list of debts with CATEGORY
-
v/$10, v/$100, v/$1000: display list of debts with amount greater than or equal $10, $100 or $1000
-
5.14. Adding a debt: adddebt
Adds a debt to the finance tracker.
Format: adddebt n/PERSON_OWED $/AMOUNT_OWED c/CATEGORY due/DEADLINE [r/REMARK]
Shortcut: ad n/PERSON_OWED $/AMOUNT_OWED c/CATEGORY due/DEADLINE [r/REMARK]
-
The PERSON_OWED should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
-
The AMOUNT_OWED should only contain positive numbers and reflect the value in dollars. Values accepted are in the range of $0.01 to $9,999,999.99. A maximum of 2 decimal places are allowed.
-
The CATEGORY is case insensitive and should only be one of the following: FOOD, TRANSPORT, SHOPPING, WORK, UTILITIES, HEALTHCARE, ENTERTAINMENT, TRAVEL, OTHERS.
-
The DEADLINE should be in dd-mm-yyyy format and should not be a date before today’s date.
-
If REMARK is omitted, no remarks will be stored.
| You can omit (optional) parameters by leaving them empty. |
Examples:
-
adddebt n/John Doe $/50.00 c/shopping due/25-02-2019 r/Loan from John to finance my new earphones -
ad n/Jane Doe $/200 c/FOOD due/03-03-2019
5.15. Editing a debt: editdebt
Edits an existing debt in the finance tracker.
Format: editdebt INDEX [n/PERSON_OWED] [$/AMOUNT_OWED] [c/CATEGORY] [due/DEADLINE] [r/REMARK]
Shortcut: ed INDEX [n/PERSON_OWED] [$/AMOUNT_OWED] [c/CATEGORY] [due/DEADLINE] [r/REMARK]
-
Edits the debt at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed debt list. The index must be a positive integer.
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
| You can omit [optional] parameters by leaving them empty. If all parameters are empty, no edits will occur. |
Examples:
-
editdebt 5 n/Tommy $/60Edits debt owed and amount owed of the 5th debt to beTommyand$60respectively.
5.16. Deleting a debt: deletedebt
Deletes the specified debt from the finance tracker.
Format: deletedebt INDEX
Shortcut: dd INDEX
-
Deletes the debt at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed debt list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
-
listdebt v/all
deletedebt 5
Deletes the 5th debt in the finance tracker.
5.17. Selecting a debt: selectdebt
Selects the specified debt from the finance tracker.
Format: selectdebt INDEX
Shortcut: sd INDEX
-
Selects the debt at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed debt list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
-
listdebt v/all
selectdebt 5
Selects the 5th debt in the finance tracker.
5.18. Clearing all debts: cleardebt
Clears all debts from the finance tracker.
Format: cleardebt
Shortcut: cd
5.19. Paying off a debt: paydebt
Converts the specified debt into an expense.
Format: paydebt INDEX [d/DATE]
Shortcut: pd INDEX [d/DATE]
-
Converts the debt at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed debt list. The index must be a positive integer.
-
After converting the debt into an expense, the debt is deleted.
-
The DATE should be in dd-mm-yyyy format and can be used to indicate actual day when user paid off the debt.
-
If DATE is omitted, current date will be used.
Examples:
-
listdebt v/all
paydebt 3
Converts the 3rd debt in the finance tracker into an expense.
5.20. Listing recurrings : listrecurring
Shows a list of recurrings in the finance tracker according to the view specified.
Format: listrecurring v/VIEW
Shortcut: lr v/VIEW
-
The VIEW specifies how the list of recurrings are displayed.
-
v/all: displays entire list of recurrings
-
v/day: displays list of recurrings with date within a day ago
-
v/month: displays list of recurrings with date within a month ago
-
v/year: displays list of recurrings with date within a year ago
-
v/CATEGORY: displays list of recurrings with CATEGORY
-
5.21. Adding a recurring: addrecurring
Adds a recurring payment to the finance tracker.
Format: addrecurring n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/START_DATE] [r/REMARK] f/FREQUENCY o/OCCURRENCE
Shortcut: ar n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/START_DATE] [r/REMARK] f/FREQUENCY o/OCCURRENCE
-
The NAME should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
-
The AMOUNT should only contain positive numbers and reflect the value in dollars. Values accepted are in the range of $0.01 to $9,999,999.99. A maximum of 2 decimal places are allowed.
-
The CATEGORY is case insensitive and should only be one of the following: FOOD, TRANSPORT, SHOPPING, WORK, UTILITIES, HEALTHCARE, ENTERTAINMENT, TRAVEL, OTHERS.
-
The START_DATE should be in dd-mm-yyyy format.
-
If START_DATE is omitted, current date will be used.
-
If REMARK is omitted, no remarks will be stored.
-
The FREQUENCY should consists of D, W, M, Y for daily, weekly, monthly and yearly respectively.
-
The OCCURRENCE should be a number from 1 to 999 inclusive.
| You can omit (optional) parameters by leaving them empty. |
Examples:
-
addrecurring n/Phone Bill $/50.00 c/utilities d/23-02-2019 r/Signed a new 2 year contract. f/M o/24 -
ar n/Magazine Subscription $/20 c/utilities f/M o/12
5.22. Editing a recurring : editrecurring
Edits an existing recurring in the finance tracker.
Format: editrecurring INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/STARTDATE] [r/REMARK] [f/FREQUENCY] [o/OCCURRENCE]
Shortcut: er INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/STARTDATE] [r/REMARK] [f/FREQUENCY] [o/OCCURRENCE]
-
Edits the recurring at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed recurring list. The index must be a positive integer.
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
| You can omit (optional) parameters by leaving them empty. If all parameters are empty, no edits will occur. |
Examples:
-
editrecurring 9 $/450 c/food
Edits the amount and category of the 9th recurring to be450andfoodrespectively.
5.23. Deleting a recurring: deleterecurring
Deletes the specified recurring from the finance tracker.
Format: deleterecurring INDEX
Shortcut: dr INDEX
-
Deletes the recurring at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed recurring list. The index must be a positive integer.
-
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
| You can omit (optional) parameters by leaving them empty. If all parameters are empty, no edits will occur. |
Examples:
-
listrecurring v/all
deleterecurring 2
Deletes the 2nd recurring in the finance tracker.
5.24. Selecting a recurring : selectrecurring
Select the specified recurring from the finance tracker.
Format: selectrecurring INDEX
Shortcut: sr INDEX
-
Selects the recurring at the specified
INDEX. -
The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed recurring list. The index must be a positive integer.
Examples:
-
listrecurring v/all
selectrecurring 2
Selects the 2nd recurring in the finance tracker.
5.25. Clearing all recurrings: clearrecurring
Clears all recurrings from the finance tracker.
Format: clearrecurring
Shortcut: cr
5.26. Converting outstanding expenses from all recurrings: convertrecurring
Converts all outstanding expenses from all recurrings in the finance tracker.
Format: convertrecurring
Shortcut: cre
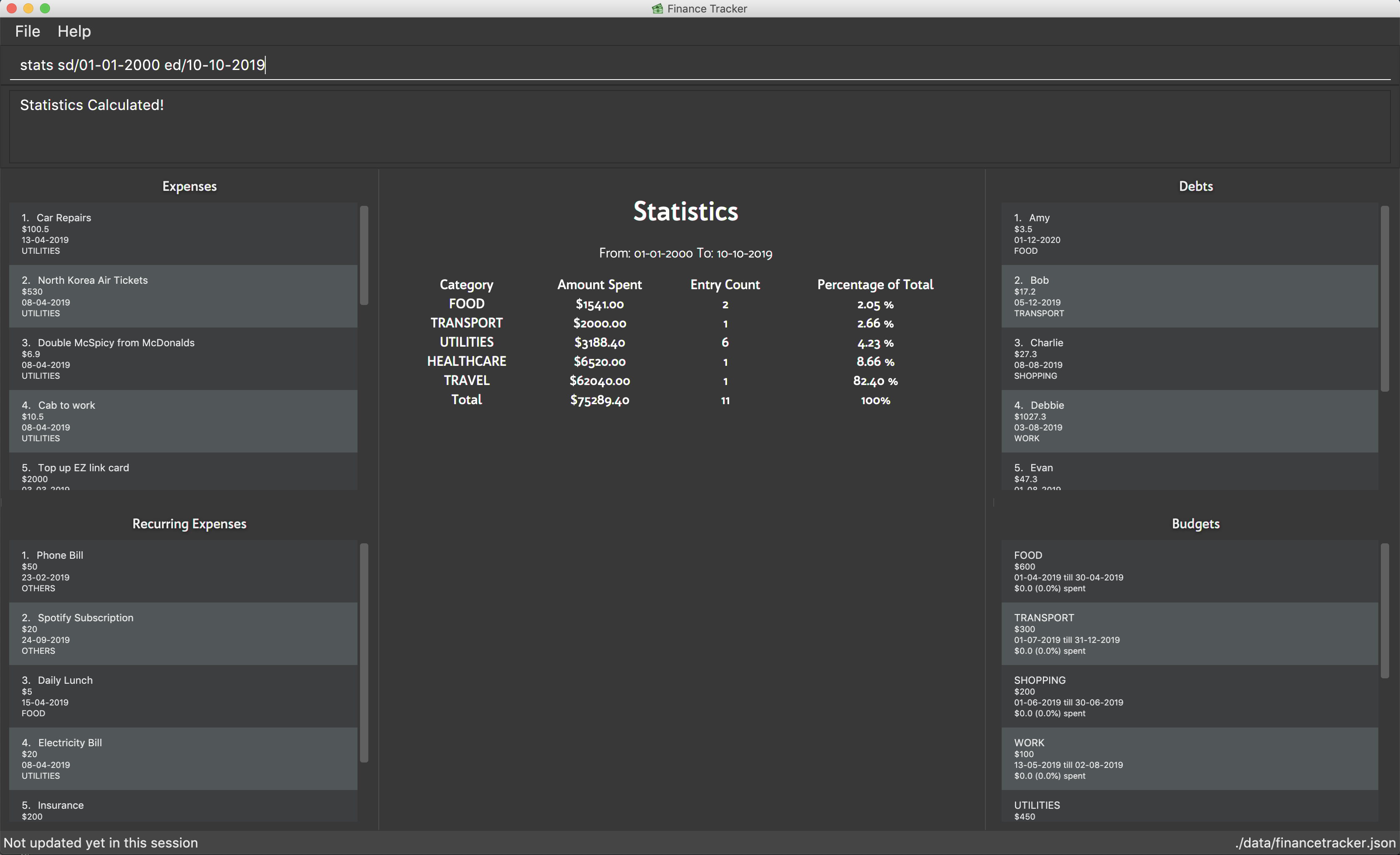
5.27. Viewing Statistics - Summary: stats
Produces statistics regarding the user’s finance.
The statistics include the frequency of entries, the total amount of money spent, and the percentage composition of the total.
The user may choose the time frame to be considered for the statistic by entering the start date and end date.
Table Example:
Category |
Amount Spent ($) |
Entry Count |
Percentage(%) |
FOOD |
302 |
38 |
13.12 |
TRANSPORT |
205 |
4 |
8.90 |
SHOPPING |
1702 |
8 |
73.96 |
WORK |
52 |
1 |
2.25 |
OTHERS |
40 |
1 |
1.92 |
Total |
2301 |
52 |
100 |
Format:
stats [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
|
Examples:
-
stats -
stats sd/12-02-2018 -
stats sd/01-01-2019 ed/01-02-2019
5.28. Viewing Statistics - Trend: statstrend
Produces statistics regarding the user’s finance over a period of time to show trends.
The statistics include the total amount of money spent on different categories and the frequency of entries in those categories.
The user must choose the time frame to be considered for the statistic by entering the start date and end date.
Table Example:
Amount ($):
Period Starting (M) |
01-01-2019 |
01-02-2019 |
01-03-2019 till End |
FOOD |
302 |
23 |
782 |
TRANSPORT |
123 |
0 |
140 |
SHOPPING |
324 |
0 |
$200 |
WORK |
0 |
401 |
0 |
TOTAL |
749 |
424 |
1122 |
Count:
Period Starting (M) |
01-01-2019 |
01-02-2019 |
01-03-2019 till End |
FOOD |
20 |
2 |
30 |
TRANSPORT |
2 |
0 |
3 |
SHOPPING |
3 |
0 |
1 |
WORK |
0 |
3 |
0 |
TOTAL |
25 |
5 |
34 |
Format: statstrend sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE f/FREQUENCY
|
Examples:
-
statstrend sd/01-01-2018 ed/01-01-2019 f/M -
statstrend sd/01-01-2018 ed/01-02-2018 f/W
5.29. Viewing Statistics - Compare: statscompare
Produces and displays statistics regarding the user’s finance for 2 time periods.
The statistics include the total amount of money spent on different categories, the frequency of entries, and the percentage composition of the total.
The user must specify 2 time periods by specifying the starting dates and the desired period length.
Table Example:
From: 01-01-2020 To: 01-01-2021
Category |
Amount Spent ($) |
Entrie Count |
Percentage(%) |
FOOD |
302 |
38 |
13.12 |
TRANSPORT |
205 |
4 |
8.90 |
SHOPPING |
1702 |
8 |
73.96 |
WORK |
52 |
1 |
2.25 |
OTHERS |
40 |
1 |
1.92 |
Total |
2301 |
52 |
100 |
From: 02-02-2019 To: 02-02-2020
Category |
Amount Spent ($) |
Entrie Count |
Percentage(%) |
FOOD |
508 |
20 |
27.16 |
TRANSPORT |
722 |
8 |
30.88 |
SHOPPING |
1003 |
32 |
42.89 |
WORK |
85 |
2 |
3.63 |
OTHERS |
20 |
1 |
0.85 |
Total |
2338 |
63 |
100 |
Format: statscompare sd1/START_DATE_1 sd2/START_DATE_2 f/FREQUENCY
|
Examples:
-
statscompare sd1/01-01-2019 sd2/01-02-2019 f/M -
statscompare sd1/01-01-2018 sd2/01-01-2018 f/D
5.30. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered, along with its index, in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
5.31. Undoing previous command : undo
Restores the finance tracker to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Format: undo
|
Undoable commands: those commands that modify the finance tracker’s content ( |
Examples:
-
deleteexpense 1
listexpense v/all
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
select 1
listexpense v/all
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
deleteexpense 1
clearexpense
undo(reverses theclearexpensecommand)
undo(reverses thedeleteexpense 1command)
5.32. Redoing the previously undone command : redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Format: redo
Examples:
-
deleteexpense 1
undo(reverses thedeleteexpense 1command)
redo(reapplies thedeleteexpense 1command) -
delete 1
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
deleteexpense 1
clearexpense
undo(reverses theclearexpensecommand)
undo(reverses thedeleteexpense 1command)
redo(reapplies thedeleteexpense 1command)
redo(reapplies theclearexpensecommand)
5.33. Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
5.34. Saving the data
Finance tracker data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
6. Coming in v2.0
6.1. Email reminders
Sends an email if the expenses are about to exceed the budget or when debts are due.
6.2. Step-by-step input
-
Taking into account non-tech savvy users not used to entering long command lines, we offer an alternative command format that prompts users to add parameters step by step.
Format: addexpense
Shortcut: ae
Examples:
-
addexpense
Please enter the name of the expense: BKT
Please enter the amount of the expense: 3.00
Please enter the category of the expense: food
Please enter the date of the expense (optional):
Please enter the remark of the expense (optional): -
editrecurring 9
Do you wish to edit previous expenses added by this recurring?: N
Please enter the name of the recurring to be updated (optional):
Please enter the amount of the recurring to be updated (optional): 450
Please enter the category of the recurring to be updated (optional): food
Please enter the frequency of the recurring to be updated (optional):
Please enter the number of occurrence of the recurring to be updated (optional):
Please enter the start date of the recurring to be updated (optional):
Please enter the remark of the expense to be updated (optional):
6.3. Statistics Visual Representation
Allows the user to view their statistics in Graphical or Pictorial formats
e.g. Pie Chart, Bar Chart
7. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Financial Tracker folder.
8. Command Summary
-
Help :
help -
History :
history -
Undo :
undo -
Redo :
redo -
List expenses :
listexpense v/VIEW -
Add an expense
addexpense n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
e.g.addexpense n/BKT $/3.00 c/food d/13-01-1996 r/My weekly bak kut teh intake -
Edit an expense :
editexpense INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/DATE] [r/REMARK]
e.g.editexpense 2 n/Bak Kut Teh -
Delete an expense :
deleteexpense INDEX
e.g.deleteexpense 3 -
Select an expense :
selectexpense INDEX
e.g.selectexpense 1 -
Clear expenses :
clearexpense -
Add a budget :
addbudget $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [sd/START_DATE] ed/END_DATE [r/REMARKS]
e.g.addbudget c/food $/400 sd/1-2-2019 ed/28-2-2019 -
Edit a budget :
editbudget c/CATEGORY [$/AMOUNT] [sd/NEW_START_DATE] [ed/NEW_END_DATE] [r/REMARKS]
e.g.editbudget c/others $/5000 sd/1-1-2019 ed/31-3-2019 -
Delete a budget :
deletebudget c/CATEGORY
e.g.deletebudget c/food -
Clear budgetss :
clearbudget -
List debts :
listdebt v/VIEW -
Add a debt :
adddebt n/PERSON_OWED $/AMOUNT_OWED c/CATEGORY [due/DEADLINE] [r/REMARK]
e.g.adddebt n/Jane Doe $/200 c/FOOD -
Edit a debt :
editdebt INDEX [n/PERSON_OWED] [$/AMOUNT_OWED] [c/CATEGORY] [due/DEADLINE] [r/REMARK]
e.g.editdebt 5 n/Tommy $/60 -
Delete a debt :
deletedebt INDEX
e.g.deletedebt 5 -
Select a debt :
selectdebt INDEX
e.g.selectdebt 1 -
Clear debts :
cleardebt -
Pay off debt :
paydebt INDEX [d/DATE]
e.g.payDebt 2 -
List recurrings :
listrecurring -
Add a recurring :
addrecurring n/NAME $/AMOUNT c/CATEGORY [d/STARTDATE] [r/REMARK] [f/FREQUENCY] [o/OCCURRENCE]
e.g.addrecurring n/Phone Bill $/50.00 c/utilities d/23-2-2019 r/Signed a new 2 year contract. f/M o/24 -
Edit a recurring :
editrecurring INDEX [n/NAME] [$/AMOUNT] [c/CATEGORY] [d/STARTDATE] [r/REMARK] [f/FREQUENCY] [o/OCCURRENCE]
e.g.editrecurring 9 $/450 c/food -
Delete a recurring :
deleterecurring INDEX
e.g.deleterecurring 2 -
Converting outstanding expenses from all recurrings :
convertrecurring
e.g.convertrecurring -
Select a recurring :
selectrecurring INDEX
e.g.selectrecurring 1 -
Clear recurrings :
clearrecurring -
Viewing Statistics - Summary:
stats [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
e.g.stats sd/01-01-2019 ed/01-02-2019 -
Viewing Statistics - Compare:
statscompare sd1/START_DATE_1 sd2/START_DATE_2 f/FREQUENCYe.g.statscompare sd1/01-01-2019 sd2/01-02-2019 f/M -
Viewing Statistics - Trend:
statstrend sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE f/PERIODe.g.statstrend sd/01-01-2018 ed/01-01-2019 f/M